
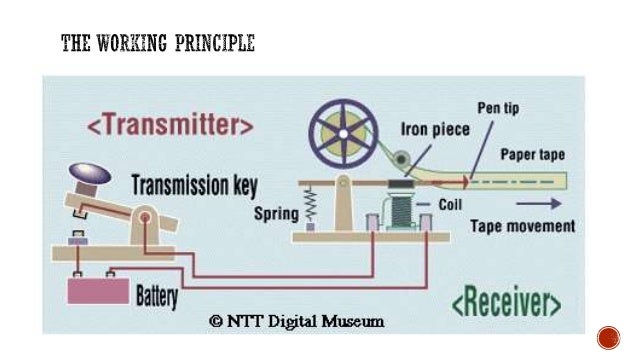
The telegraph has been in use for more than 150 years. The prototype of the telegraph was demonstrated by Joseph Henry in 1830. He transmitted an electric current over a length of wire approximately 1 mile (1.6 kilometer) in length to activate a bell on the opposite end of the circuit. This device was refined and developed by Samuel F. B. Morse into a system that used a solenoid, equipped with a marker, to record multiple pulses of varying duration on a moving strip of paper. These pulses appeared as so-called dots and dashes. Patterns of these dots and dashes were assigned to letters of the alphabet, single-digit numerals, and punctuation marks. On May 1, 1844, the first official telegraph message was sent.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario